The dielectric substance of silent discharge (i.e., dielectric barrier discharge) is an important component of the silent discharge ozone generator. Its function is to strengthen the electric field strength of the air gap to facilitate discharge; prevent the breakdown of the air gap and reduce power consumption; make the electric field of the air gap uniform and expand the discharge area, which is beneficial to the generation of ozone. Generally speaking, the higher the dielectric coefficient of the dielectric substance, the better the thermal conductivity, the better it is to produce ozone. The dielectric substance used in ozone generators mainly include quartz glass, ceramics, enamel, organic materials and other types.
Some of the existing ozone generator dielectric substance use insulating materials such as glass and enamel. These materials have poor dielectric properties and high voltage resistance. The thickness of these dielectric substance generally is close to or greater than 1 mm, and some are even thicker. This type of material has poor heat dissipation performance, and the heat dissipation problem has become a major difficulty for this type of ozone generator. Generally, it is necessary to consider leaving a larger space for heat dissipation or design a special cooling system, which result in a bulky ozone generator.
By caparison, high-purity alumina ceramic substrates are excellent used as dielectric substance with the following characteristics:
 Excellent in insulation properties Excellent in insulation properties
|
 Small dielectric constant Small dielectric constant
|
 Excellent in thermal shock resistance Excellent in thermal shock resistance
|
 Good smoothness / flatness Good smoothness / flatness
|
 High thermal conductivity High thermal conductivity
|
 Thermal expansion coefficient similar to silicon Thermal expansion coefficient similar to silicon
|
 Excellent resistance against oil / acid / alkali Excellent resistance against oil / acid / alkali
|
 ... ...
|
Properties of Alumina ceramic substrate:
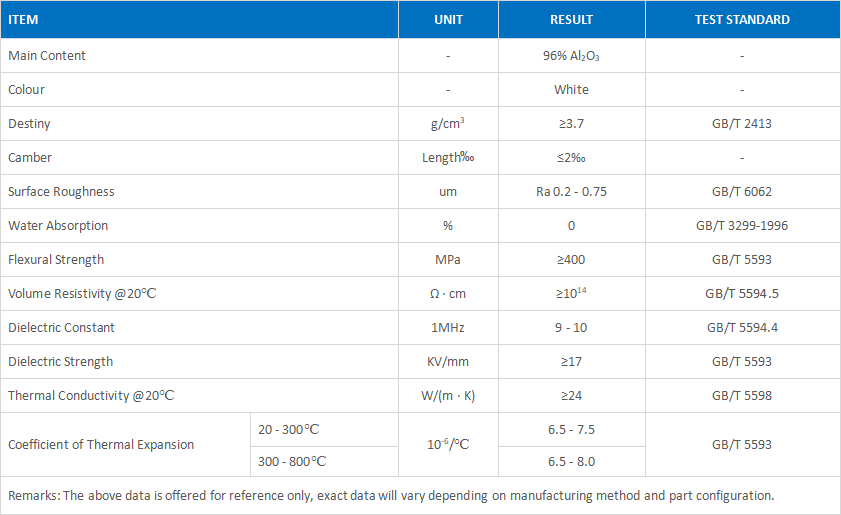
Due to the good thermal conductivity, the alumina ceramic substrate can better dissipate the heat generated by the ozone generator during operation, and will not decompose the ozone generated due to the increase in temperature, thus ensuring the stable generation of ozone and reducing the heat dissipation measures. The requirements of high-purity alumina simplifies the structure; high-purity alumina ceramics are strong, its strength and toughness are better than those of glass, and its physical and chemical properties are stable, which is conducive to thinning and downsizing. Alumina ceramics have a large dielectric constant, good insulation performance, and high voltage resistance, which can be used under high electric field strength.
In recent years, dielectric layer materials and processing technology have become the key technology for dielectric barrier strong ionization discharge. Plasma spraying or pasting method is used to form an extremely thin dielectric layer of dense Al2O3 material on the surface of the discharge electrode and ground electrode of 400~1600cm2. It has the characteristics of high strength, high density, high insulation, high dielectric constant, high uniformity, low curvature and low loss. The relevant parameters that can be achieved by using this technology are: critical breakdown electric field strength E≥400kV/cm; relative permittivityε≥10; volume resistivityρ≥1015Ψcm; dielectric loss tanδ<3.9×10-4; volume density n≥3.8g/cm3; thermal conductivityλ≥21W/(Km); thermal expansion coefficient (6.5~7.5)×10-6mm/°C; surface roughness 0.25~0.5μm; water absorption tends to 0; medium thickness 0.1mm; The maximum area of dielectric <1600cm2.








 Small dielectric constant
Small dielectric constant
























