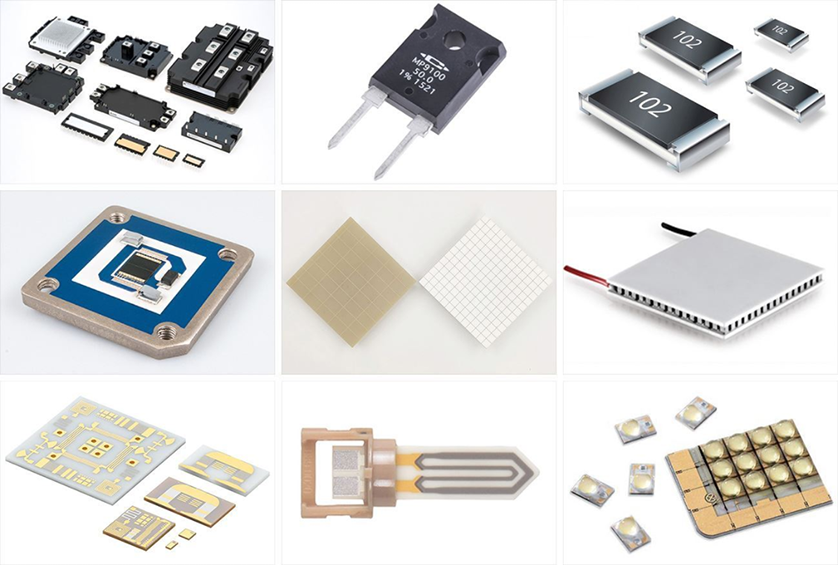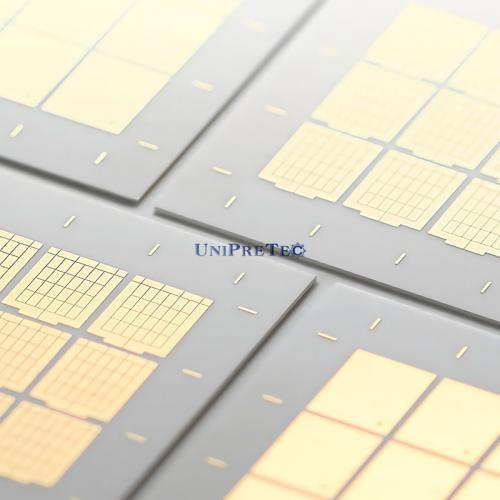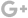
● Description of DPC Ceramic Substrates
Two common processing technology for metallized ceramic substrates are DBC (Direct Bonded Copper) and DPC (Direct Plated Copper). However, due to the reduced size of used components and the higher requirements for dimensional accuracy, DBC is becoming increasingly insufficient. Therefore, DPC replaces DBC as the main ceramic substrate metallization technology, which has received more and more attention. In order to provide customers with higher quality ceramic substrate products, UNIPRETEC has invested significant time and resources in R&D and innovation to advance DPC technology.
Thin-film circuit ceramic packaging substrate is a technology that uses magnetron sputtering thin-film metallization and electroplating process: that is, according to application needs, on a ceramic substrate with high thermal conductivity, thin-film metallization and image transfer methods are used to make 2D metal circuits, and then use TCV (Through Ceramic Via) technology forms vertical interconnections between double-sided wiring, and finally uses stacking technology to obtain a one-piece 3D metal frame that is tightly bonded to the ceramic matrix. Based on the thin film circuit process, the ceramic surface is metallized by magnetron sputtering, and the thickness of the copper layer and gold is more than 10 microns by electroplating, that is, DPC (DirectPlateCopper-direct copper plating substrate).
As a circuit board, metallized ceramic substrates have high heat resistance and a thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of semiconductors. The ceramic substrate is suitable for high-brightness LED, solar energy and other high-power products, with excellent weather resistance, and is also suitable for harsh outdoor environments. Due to its good chemical stability, non-toxic and lead-free, it is not harmful to the environment. Therefore, the application of ceramic substrates in various industries has become more common and popular.
● Advantages of Our DPC Ceramic Substrates
√ Good Solderability
|
√ Conductive Layer Can Be Within 1um~1mm Thick
|
√ Stronger, Lower Resistance Metal Coating
|
√ Minimum Curcuit Line Distance Reaches 0.05mm
|
√ Extremely High Service Temperature
|
√ Copper Surface Without Thermal Oxide Coating
|
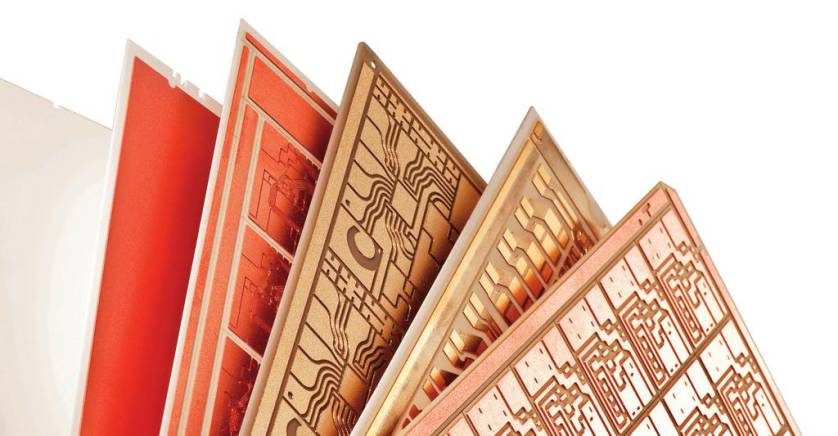

● Properties of Ceramic Substrates
ITEM
|
UNIT
|
A960
|
ALN
|
Main Content
|
-
|
Al2O3 > 96%
|
AlN > 95%
|
Density
|
g/cm3
|
> 3.7
|
> 3.3
|
Color
|
-
|
White
|
Grey
|
Water Absorption
|
%
|
0
|
0
|
Warpage
|
-
|
< 2‰
|
< 2‰
|
Standard Surface Roughness (Ra)
|
um
|
0.2 - 0.7
|
0.3 - 0.6
|
Flexural Strength
|
Mpa
|
380
|
440
|
Thermal Conductivity (25 °C)
|
W/m.K
|
> 25
|
> 175
|
Thermal Expansion Coefficient (25 - 300 °C)
|
10-6 mm/°C
|
6.5 - 7.5
|
2 - 3
|
Thermal Expansion Coefficient (300 - 800 °C)
|
10-6 mm/°C
|
6.5 - 8.0
|
2.5 - 3.5
|
Max. Working Temperature
|
°C
|
1,200
|
1,200
|
Dielectric Strength
|
KV/㎜
|
> 17
|
> 17
|
Dielectric Constant
|
1 MHz
|
9 - 10
|
17
|
Electrical Resistivity (25 °C)
|
Ω·cm
|
> 1014
|
> 1014
|
∆ The data is offered for reference only, exact data will vary depending on producing method & part configuration.
● Applications of DPC Ceramic Substrates
DPC ceramic substrates are recommended for power electronic modules (e.g. current inverters) using MOSFETs or IGBT semiconductor elements and diodes for widespread application fields in the industrial sector: electric motor drives, e.g. in tooling machines, cranes, textile-processing equipment, automation equipment, etc.
As high-performance circuit carriers for power electronic applications: In such groups as power steering, start-stop systems, air conditioning compressors, water pumps, oil pumps, brakes, etc; Converters for hybrid or electrical power train; Battery chargers; Inductive charging systems; DC-DC converters; Rail vehicles such as locomotives, subway trains, trams and cable cars, etc; Communications.